Description
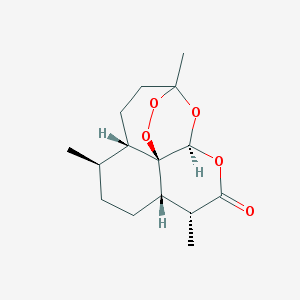
Artemisinin, popularly known as sweet wormwood, is a naturally occurring chemical obtained from the plant Artemisia annua. It is a powerful antimalarial drug that has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for millennia to treat fever and other diseases.
Artemisinin and its derivatives, such as artesunate, are thought to be among the most effective antimalarial medications on the market, particularly for the treatment of severe and drug-resistant malaria. The chemical kills the malaria parasite by creating toxic-free radicals in its cells.
Artemisinin has also demonstrated potential in the therapy of other disorders, like as cancer. Artemisinin and its derivatives have been shown in studies to selectively kill cancer cells while sparing healthy cells, and they may be useful against a range of cancer types, including breast, lung, and prostate cancer.
Main Benefits of Artemisinin:
- Effective Malaria Treatment: Artemisinin is most renowned for its effectiveness against malaria, particularly against strains resistant to other drugs. It works by attacking the malaria parasites in the blood, reducing the severity and duration of the infection.
- Rapid Action: Compared to other antimalarial drugs, artemisinin acts quickly, bringing down fever and parasitic levels in the blood within a short period.
- Versatility in Drug Combinations: Artemisinin is often used in combination with other antimalarial drugs, in what’s known as Artemisinin-based Combination Therapies (ACTs). These combinations are more effective and reduce the risk of developing resistance.
- Potential Beyond Malaria: Research indicates potential benefits of artemisinin in treating certain cancer types, though this application is still in the experimental stages.
Applications:
- Malaria Treatment: The primary application of artemisinin is in the treatment of malaria, particularly in areas where the disease is prevalent, and other treatments have failed due to drug resistance.
- Combination Therapies: In ACTs, it’s combined with other drugs like mefloquine, lumefantrine, or amodiaquine to enhance efficacy and combat drug resistance.
- Research in Other Diseases: While still in early stages, research is exploring the use of artemisinin in treating autoimmune diseases and certain types of cancer, showing its potential versatility in the medical field.