Description
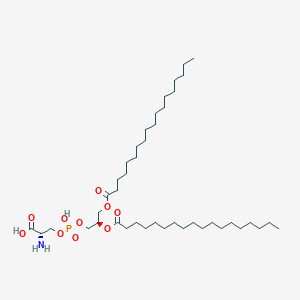
Phosphatidylserine (PS) is a phospholipid and a key component of the cell membrane. It is particularly abundant in the brain and is important for maintaining cellular function, especially in neurons.
Function
In biological membranes, phosphatidylserine plays a key role in cell cycle signaling, specifically in relationship to apoptosis. It has several vital functions within the body:
- Cellular Structure: As a building block of cell membranes, it helps to maintain the fluidity and integrity of cells.
- Signaling: It is involved in signaling cascades of the cell, particularly because it can act as a site for the attachment of proteins involved in cell signaling.
- Apoptosis: PS is involved in the process of programmed cell death (apoptosis). It is normally located on the inner layer of the cell membrane, but during the early stages of apoptosis, PS is transferred to the outer layer of the membrane, where it acts as a signal for the initiation of phagocytosis of the dying cell.
- Blood Coagulation: PS exposure on the outer leaflet of cell membranes is also a key step in the process of blood coagulation.
Application and Benefits
Phosphatidylserine has been researched for its potential applications in various health conditions and situations:
- Cognitive Function and Brain Health: Supplements of PS have been studied for their potential to support cognitive functions, such as memory and concentration, especially in the elderly. There is some evidence to suggest that PS can help alleviate cognitive decline.
- Athletic Performance: There is interest in using PS to help reduce muscle soreness and improve exercise performance, though results from studies are mixed.
- Mood and Stress: Some research has suggested that PS might help reduce stress and improve mood. It might be particularly beneficial in reducing the effects of exercise-induced stress.
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Although not conclusively proven, PS has been examined for its potential benefits in slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
Safety and Considerations
Phosphatidylserine is generally considered safe when taken as a supplement, but it’s always best to talk with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
Dietary Sources
Phosphatidylserine can be found in certain foods, such as soybeans, egg yolks, chicken liver, and Atlantic mackerel. The body can also synthesize it.