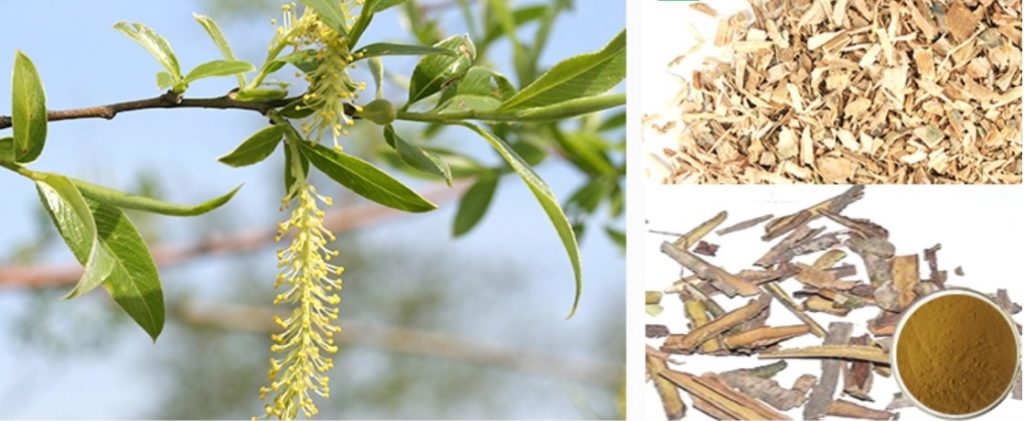
Description
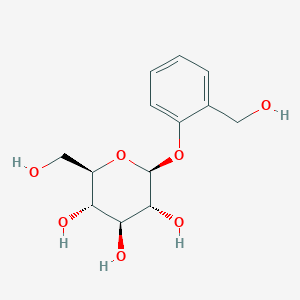
Salicin is a type of alcoholic -glucoside. Salicin is an anti-inflammatory agent that is produced in (and called after) willow (Salix) bark. Salicin can also be found in the bark of Populus species as well as the foliage of willows and poplars. Castoreum, which was used as a painkiller, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic, also contains it. Salicin is chemically similar to aspirin and has a very similar effect in the human body. Salicin is metabolized into salicylic acid when ingested by humans.
Willow bark includes salicin, which your body converts into another chemical substance called salicylic acid. Salicylic acid, like acetylsalicylic acid, reduces the production of certain prostaglandins (hormone-like substances that regulate your immune system and combat joint inflammation) in your nerves, which relieves pain and discomfort. Several laboratory experiments found that willow bark has anti-inflammatory properties.
Salicin has been studied as a potent antiinflammatory agent. Angiogenesis is an essential process for tumor progression, and negative regulation of angiogenesis provides a good strategy for antitumor therapy. However, the potential medicinal value of salicin on antitumorigenic and antiangiogenic effects remain unexplored. In this study, we examined the antitumorigenic and antiangiogenic activity of salicin and its underlying mechanism of action. Salicin suppressed the angiogenic activity of endothelial cells, such as migration, tube formation, and sprouting from an aorta. Moreover, salicin reduced reactive oxygen species production and activation of the extracellular signal‐regulated kinase pathway. The expression of vascular endothelial growth factor was also decreased by salicin in endothelial cells. When the salicin was administered to mice, salicin inhibited tumor growth and angiogenesis in a mouse tumor model. Taken together, salicin targets the signaling pathways mediated by reactive oxygen species and extracellular signal‐regulated kinase, providing new perspectives into a potent therapeutic agent for hypervascularized tumors. — John Wiley & Sons
Salicin from FreShine Chemicals: White Willow Bark Extract, 25%-98% .