Description
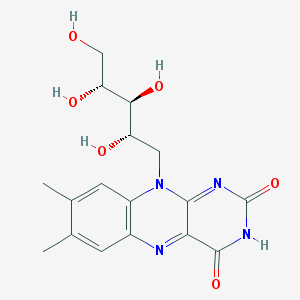
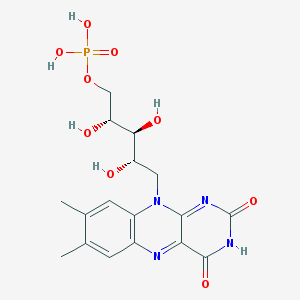
Vitamin B2, also known as Riboflavin, is one of eight B vitamins that are essential for human health. It is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in energy production and the metabolism of fats, drugs, and steroids. The body needs riboflavin to maintain health, but it cannot store it in large amounts, so people need to consume it regularly in their diets.
Functions of Riboflavin:
- Energy Production: Riboflavin is integral to the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the currency of energy in our bodies. It acts as a coenzyme with other B vitamins to convert carbohydrates into glucose for energy.
- Cellular Function and Growth: It is involved in the growth and development of body cells including the red blood cells and it supports cell function by working as a coenzyme to support the metabolism of fats, drugs, and steroids.
- Skin and Eye Health: Riboflavin is crucial for maintaining healthy skin and mucous membranes. It also contributes to good vision and can reduce the risk of developing cataracts.
- Antioxidant Role: As a component of the enzyme glutathione reductase, riboflavin helps recycle glutathione, an important antioxidant that protects cells from damage by free radicals.
Applications of Riboflavin:
- Dietary Supplements: Riboflavin is commonly included in multivitamin and B-complex supplements to prevent and treat riboflavin deficiency.
- Fortification: Many countries fortify breads and cereals with riboflavin as a public health measure to ensure adequate intake among the population.
- Clinical Treatment: It is used in the clinical treatment of various conditions, including riboflavin deficiency, migraine headaches, and some eye disorders.
- Research Tool: Riboflavin, due to its fluorescent properties when exposed to UV light, is used as a tracer in various scientific research applications.
Benefits of Riboflavin:
- Prevention of Riboflavin Deficiency: Adequate intake of riboflavin is necessary to prevent riboflavin deficiency, which can lead to symptoms such as sore throat, redness and swelling of the lining of the mouth and throat, anemia, and skin disorders.
- Migraine Relief: Some studies suggest that riboflavin supplementation may be beneficial for people with migraines by decreasing the frequency of attacks.
- Energy Levels: By playing a key role in the conversion of food into energy, riboflavin can contribute to overall increased energy levels.
- Eye Health: Regular intake of riboflavin, along with other nutrients, is thought to maintain eye health and possibly reduce the risk of cataracts.
Dietary Sources of Riboflavin:
Riboflavin is found in various foods, including:
- Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt.
- Lean meats and eggs.
- Green vegetables such as spinach, asparagus, and broccoli.
- Whole and enriched grains and cereals.