Description
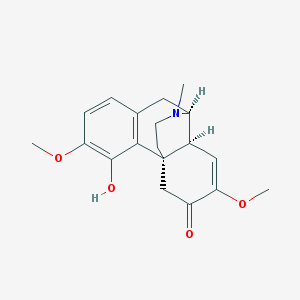
Sinomenine, also known as cocculine, is an alkaloid found in the root of the Japanese and Chinese climbing plant Sinomenium acutum. In these countries, the plant has traditionally been used in herbal medicine to treat rheumatism and arthritis. Sinomenine has been shown to have low cytotoxicity and a wide range of biological activities, including anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and anti-arthritic properties.
Here are the main benefits and applications of Sinomenine:
- Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Effects: Sinomenine is noted for its potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic (pain-relieving) properties. This makes it potentially useful in the treatment of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, as it can help reduce joint swelling and alleviate pain.
- Immunomodulatory Properties: It has been shown to have effects on the immune system, which can be beneficial in treating autoimmune diseases. Its immunomodulatory action can help in regulating immune responses, thus providing therapeutic benefits in conditions where the immune system is involved.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Research indicates that Sinomenine may have neuroprotective effects, suggesting potential applications in neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. It may help in protecting nerve cells from damage and improving neurological functions.
- Cardiovascular Benefits: There is some evidence to suggest that Sinomenine can have beneficial effects on the cardiovascular system, including improving blood circulation and potentially reducing the risk of certain heart diseases.
- Anti-Cancer Potential: Preliminary studies have indicated that Sinomenine may possess anti-cancer properties, inhibiting the growth of certain types of cancer cells. However, more research is needed to establish its efficacy and safety in cancer treatment.
- Respiratory Conditions: It may also be useful in treating certain respiratory conditions due to its anti-inflammatory properties, helping to reduce inflammation in the respiratory tract.