Description
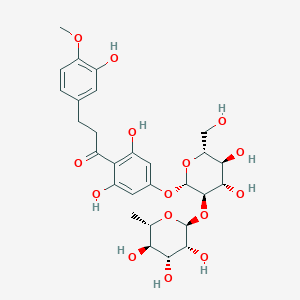
Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone, also known as neohesperidin DC or simply NHDC, is a concentrated non-nutritive sweetener derived from neohesperidin, a naturally occurring bitter-tasting flavanone found in citrus fruit. It is well known for having a strong synergistic effect when used in conjunction with other artificial sweeteners.
Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone (NHDC) is a sweetener derived from citrus, specifically from a flavonoid found in bitter oranges. It is known for its intense sweetness, which is estimated to be about 1500-1800 times sweeter than table sugar (sucrose). Here are some of its key benefits and applications:
Benefits of Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone
- Intense Sweetness: Its high sweetness potency means that it can be used in very small amounts, reducing the calorie content in foods and beverages.
- Taste Modification: NHDC is also known for its ability to mask bitter flavors, making it valuable in pharmaceuticals and food products that have an inherent bitterness.
- Stability: It is stable under heat and over a broad range of pH levels, making it suitable for various processing conditions.
- Non-Cariogenic: Unlike traditional sugars, NHDC does not contribute to tooth decay, making it a better choice for oral health.
Applications of Neohesperidin Dihydrochalcone
- Food and Beverages: Used as a sweetener in a wide range of products such as soft drinks, juices, dairy products, desserts, and candies.
- Pharmaceuticals: Employed in masking the bitter taste of active pharmaceutical ingredients in syrup formulations, tablets, and chewable medicines.
- Nutraceuticals and Dietary Supplements: Incorporated in supplements, particularly those that need a sweetness boost without added calories.
- Oral Care Products: Utilized in toothpaste and mouthwash for its sweetness and non-cariogenic properties.