Description
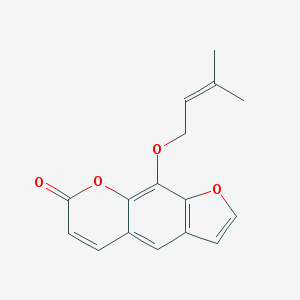
Imperatorin is a natural compound found in several plants, including angelica, grapefruit, and bergamot. It belongs to the family of furocoumarins, which are organic compounds containing a fused ring structure called a furan ring and a coumarin ring.
Imperatorin has been traditionally used in Chinese medicine for its anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, and analgesic properties. In recent years, it has gained attention for its potential therapeutic effects on various health conditions, including neurological disorders, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.
Imperatorin is a naturally occurring chemical compound classified as a furanocoumarin. It’s primarily found in plants of the Apiaceae family, such as Angelica archangelica and Pastinaca sativa. Imperatorin is known for its various pharmacological effects, including:
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Imperatorin has been shown to reduce inflammation, making it potentially beneficial for treating inflammatory conditions.
- Antispasmodic Effects: It helps in relaxing smooth muscles, which can alleviate spasms and cramps.
- Antimicrobial Activity: Imperatorin exhibits antimicrobial properties, effective against a range of bacteria and fungi.
- Neuroprotective Effects: It may protect nerve cells from damage and is being studied for its potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases.
- Anticancer Potential: Some studies suggest that imperatorin can inhibit the growth of certain cancer cells, but more research is needed in this area.
- Phototoxicity: In traditional medicine, imperatorin is used in phototherapy for skin diseases due to its photosensitizing properties.
In terms of application, imperatorin is used in:
- Traditional Medicine: It has been used in traditional medicinal practices for various ailments, particularly in Chinese and Ayurvedic medicine.
- Pharmaceuticals: Research is ongoing to harness its potential in developing new drugs, especially for anti-inflammatory and anticancer treatments.
- Cosmetics: Due to its phototoxic properties, it’s sometimes used in skincare, particularly in products that aim to treat certain skin conditions.