Description
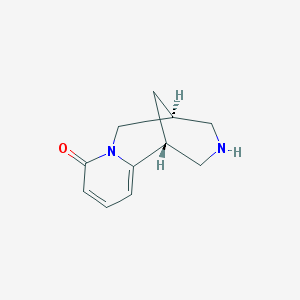
Cytisine, also known as baptitoxine and sophorine, is an alkaloid found in several plant species, including Laburnum and Cytisus of the Fabaceae family. It has been used therapeutically to aid in the cessation of smoking. It has a comparable molecular structure to nicotine and has similar pharmacological effects.
Cytisine, like varenicline, is a partial activator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. (nAChRs). Cytisine has a 4.8-hour half-life and is quickly eliminated from the body. Outside of Eastern Europe, the use of cytisine for smoking cessation is still comparatively unknown.
Benefits:
- Smoking Cessation: The primary benefit of Cytisine is its effectiveness in helping people quit smoking. It acts on the brain similarly to nicotine, reducing the severity of withdrawal symptoms and cravings for nicotine.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to other smoking cessation aids like varenicline (Chantix), cytisine is generally more affordable, making it accessible to a wider range of people.
Application:
Cytisine is typically administered orally in tablet form. The course of treatment usually spans 25 days, with the dosage gradually decreasing over this period. Users start with a higher dose, which is slowly reduced as their dependency on nicotine decreases.
Main Usage:
The main usage of Cytisine is to aid in smoking cessation. It’s particularly effective because it binds to the same brain receptors as nicotine, thus mimicking the effects of nicotine to some extent and easing withdrawal symptoms. This pharmacological action helps smokers reduce their nicotine intake gradually and eventually quit smoking.