Description
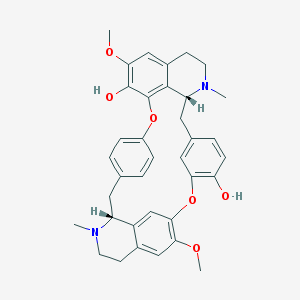
Curine is a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid isolated from the plant Chondrodendron platyphyllum which is used to treat malaria, inflammation, and pain.
Curine induces cell cycle arrest and cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and may also have an anti-allergic effect. It is described to noncompetitively block neuromuscular transmission through interaction with the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.
Curine is a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloid extracted from plants in the Menispermaceae family, particularly from Chondrodendron tomentosum and Strychnos toxifera. This compound has gained attention due to its various pharmacological properties.
Main Benefits of Curine:
- Anticancer Properties: Curine has shown promising results in inhibiting the growth of cancer cells. It works by inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancerous cells, which can be beneficial in the treatment of various types of cancer.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: The compound exhibits significant anti-inflammatory activities. It can inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines and mediators, making it potentially useful in treating conditions like arthritis and other inflammatory diseases.
- Antimicrobial Activity: Curine has been found to possess antimicrobial properties against a range of bacteria and fungi. This makes it a potential candidate for developing new antimicrobial agents, especially in an era where resistance to conventional antibiotics is a growing concern.
- Antispasmodic Effects: Due to its muscle relaxant properties, curine can be used to relieve spasms, particularly in smooth muscle tissues. This makes it potentially useful in treating conditions like asthma, where smooth muscle constriction is a problem.
- Neuroprotective Properties: There’s emerging evidence that curine may have neuroprotective effects, which could be beneficial in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Applications:
- Pharmaceuticals: Given its range of biological activities, curine is being explored for development into various pharmaceutical formulations for cancer therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and antimicrobial agents.
- Research Tool: In biomedical research, curine is used as a tool to study cellular processes like apoptosis and inflammation.
- Herbal Remedies: In traditional medicine systems, plant extracts containing curine are used for their medicinal properties, though it’s important to note that such uses should be approached with caution due to the potential for toxicity and lack of standardized dosing.