Description
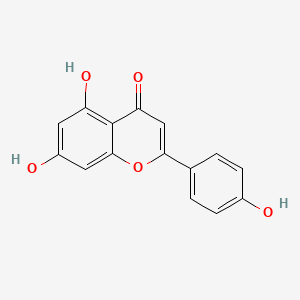
Apigenin is a natural bioactive flavonoid compound found in a wide variety of plant sources. Chemically, it’s identified as 4′,5,7-trihydroxyflavone, and its molecular formula is C₁₅H₁₀O₅. This compound gives certain flowers and vegetables their vibrant colors.
Sources: Apigenin is primarily found in:
- Parsley
- Celery
- Chamomile
- Oranges
- Grapefruits
- Onions
- Wheat sprouts
- Tea (especially chamomile tea)
Applications:
- Dietary Supplements: Given its potential health benefits, apigenin is often included in dietary supplements.
- Cosmetic Products: Due to its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-cancer properties, apigenin is used in skincare and cosmetic products.
- Research Tool: Scientists use apigenin in research, particularly in cancer research, to study its impact on cell signaling and its potential anti-tumor effects.
Benefits:
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Apigenin has shown potential in reducing inflammation by inhibiting the production of certain pro-inflammatory cytokines.
- Antioxidant Activity: Like many flavonoids, apigenin is a potent antioxidant that can protect cells from damage by free radicals.
- Anti-cancer Properties: Some studies suggest that apigenin can inhibit cancer cell growth and proliferation. It has shown potential anti-cancer effects against several types of cancers including breast, digestive tract, skin, prostate, and blood cancers.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Research indicates that apigenin may support brain health and counteract neuroinflammatory conditions. Some studies also hint at its potential in reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Anti-anxiety Effects: A study in mice has suggested that apigenin can produce mild anti-anxiety and mild sedative effects, which could be why chamomile tea, rich in apigenin, is often touted for its relaxing properties.
- Beneficial for Cardiovascular Health: Apigenin may support heart health by improving blood vessel function and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Supports Immune System: Some studies indicate that apigenin can modulate the immune response, potentially benefiting conditions like autoimmune diseases.