Description
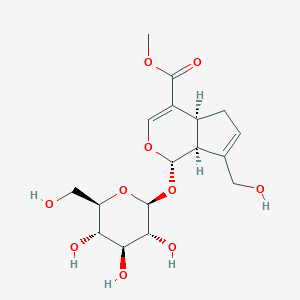
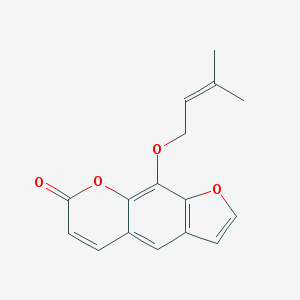
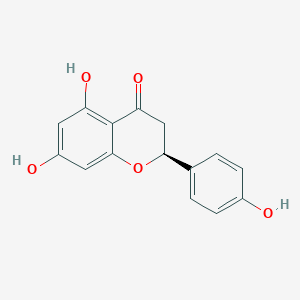
Tea saponins, found in Camellia plants, are natural non-ionic surfactants with obvious soil remediation benefits. The majority of tea saponins are extracted from Camellia oleifera seed meal, with Camellia sinensis leaves and flowers as potential sources.
Tea saponins are natural surfactants found in tea seeds, which are the seeds of the Camellia sinensis plant. They are a type of glycoside, a large group of organic compounds widely distributed in the plant kingdom. Tea saponins have a variety of beneficial properties and applications:
- Biodegradability: One of the most significant advantages of tea saponins is their biodegradability. They are an environmentally friendly alternative to synthetic surfactants.
- Pesticidal Properties: Tea saponins have been used as natural pesticides. Their ability to disrupt the cell membranes of various pests makes them effective in controlling insects and pathogenic fungi in agriculture.
- Aquaculture: In aquaculture, tea saponins are used to eliminate unwanted fish and snails from ponds. They help in maintaining the balance of aquatic ecosystems without harming the environment.
- Detergents and Cleaners: Due to their surfactant nature, tea saponins are used in the production of detergents and cleaners. They help in reducing surface tension, thus improving the cleaning efficiency.
- Foaming Agent: Tea saponins are excellent foaming agents, making them useful in products that require lather, such as shampoos and soaps.
- Antioxidant Properties: They exhibit antioxidant properties, which can be beneficial in skincare and health products, helping to protect the skin and body from free radicals.
- Cholesterol-Lowering Effects: Studies have shown that tea saponins can reduce cholesterol levels in the body, contributing to heart health.
- Anti-inflammatory and Antimicrobial Effects: They also have anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, which can be utilized in pharmaceuticals and skincare products.
- Feed Additive: In animal nutrition, tea saponins are added to feed to improve nutrient absorption and promote animal health.
- Emulsifying Properties: Their ability to emulsify fats makes them useful in food and beverage industries, particularly in products like salad dressings and sauces.