Description
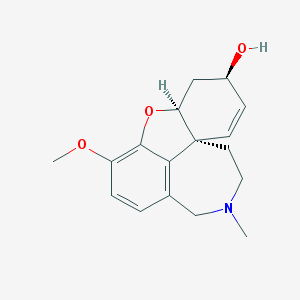
Galanthamine is a natural alkaloid that is extracted from the bulbs of certain species of snowdrop plants, particularly Galanthus nivalis. It is also found in other members of the Amaryllidaceae family, such as Narcissus and Leucojum.
Galanthamine is a reversible and competitive inhibitor of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE), which breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the brain. By inhibiting AChE, galanthamine increases the concentration of acetylcholine in the brain, which can improve cognitive function and memory.
Galanthamine is used as a medication for the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. It is believed to improve cognitive function by enhancing the transmission of nerve impulses in the brain. It may also have neuroprotective effects by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation.
Galanthamine has been used for medicinal purposes for centuries, particularly in traditional Chinese and Bulgarian medicine. In recent years, it has gained attention as a potential treatment for other conditions, such as myasthenia gravis, a neuromuscular disorder characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue. It has also been studied for its potential use in the treatment of schizophrenia and depression.