Description
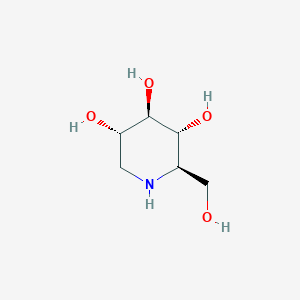
1-Deoxynojirimycin (DNJ) is a naturally occurring chemical found in plants such as the mulberry tree (Morus alba) and the soybean plant. (Glycine max). It is an iminosugar, a type of molecule recognized for inhibiting the activity of particular enzymes in the body.
DNJ has being researched for its possible therapeutic use, particularly in the treatment of diabetes. It acts by suppressing the action of alpha-glucosidase, an enzyme that breaks down carbs into glucose. By inhibiting this enzyme, DNJ can assist to limit glucose absorption from the digestive system and hence lower blood sugar levels.
DNJ has being researched for its possible application in the treatment of other disorders, including obesity, high cholesterol, and neurodegenerative diseases, in addition to its potential benefits for diabetes management.
It has garnered significant attention for its potential health benefits and applications. Here are the key aspects:
- Blood Sugar Regulation: DNJ is known for its ability to regulate blood sugar levels. It inhibits alpha-glucosidase, an enzyme involved in the digestion of carbohydrates. By slowing down the digestion of carbohydrates, it can help prevent spikes in blood sugar levels, making it potentially beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes.
- Antiviral Properties: DNJ has shown promise in its antiviral activity, particularly against viruses like HIV and hepatitis B. It interferes with the glycosylation process in viral cells, which is crucial for the maturity and infectivity of these viruses.
- Weight Management: Due to its effects on carbohydrate digestion, DNJ may aid in weight management. By slowing carbohydrate absorption, it can promote a feeling of fullness and reduce overall calorie intake.
- Gastrointestinal Health: DNJ may contribute to gastrointestinal health by affecting the gut microbiota. It can promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which is important for overall gut health.
- Cholesterol Management: Preliminary research suggests that DNJ might have a role in managing cholesterol levels, although more research is needed in this area.
- Applications in Food and Supplements: DNJ is used in various food products and dietary supplements. It is often marketed for its potential benefits in blood sugar regulation and weight management.
- Research and Development: DNJ is the subject of ongoing research, particularly in the fields of diabetes management, viral infections, and metabolic health.