Description
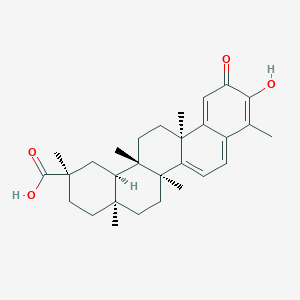
Tripterine is a chemical substance extracted from the roots of Tripterygium wilfordii and Celastrus regelii. Celastrol is a pentacyclic triterpenoid that corresponds to the quinone methide family.
Tripterine has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and insecticidal properties in in vitro and in vivo rodent studies. It has been shown in rodents to have anti-obesity properties. Tripterine has also been shown to have anti-diabetic effects on diabetic nephropathy and to reduce whole-body insulin resistance (via inhibition of NF-B in the hypothalamus).
Benefits of Tripterine:
- Anti-inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects: Tripterine has been shown to have significant anti-inflammatory effects, which can be beneficial in treating autoimmune diseases.
- Anticancer Properties: Research indicates that tripterine may inhibit the growth of various cancer cells, making it a potential candidate for cancer therapy.
- Neuroprotective Effects: Studies suggest that tripterine may have neuroprotective properties, offering potential benefits in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Applications of Tripterine:
- Medical Research: Tripterine is primarily used in scientific research to explore its therapeutic potential in various diseases.
- Pharmaceutical Development: There is ongoing research into developing tripterine-based medications for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and certain cancers.
Main Usage:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment: One of the main uses of tripterine is in the treatment of autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, where its anti-inflammatory properties can be particularly beneficial.
- Experimental Cancer Treatment: While still in the research phase, tripterine is being explored as a treatment option for various types of cancer due to its ability to induce apoptosis (cell death) in cancer cells.